The cost of owning and managing IT infrastructure and data services is enormous. Maintaining the infrastructure alone requires a heavy investment in hardware, software, and databases. And since many companies consider that very expensive, they choose to store their data in the cloud and pay for cloud computing services like storage, networking, software, servers, business intelligence, and analytics on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Through this process of cloud computing, they avoid the complexity and cost that comes from running and maintaining their own data centers or IT infrastructure. To understand this better, we will begin with a cloud computing definition.
What is Cloud Computing?

Generally‚ cloud computing is a term for anything that has to do with delivering hosted services over the internet. In simple terms‚ it means the storage and accessing of files and programs in the cloud while eliminating the need to use physical hardware and direct management by the user.
In other words‚ with cloud computing‚ users can access their files and documents everywhere‚ (not just in the computer the data originated from) as the data is on a network of hosted servers that are transmitting data over the internet.
Why is it Called Cloud Computing?
The word “cloud” stands for the internet. If a company moves to the cloud‚ it means that their data and IT infrastructure are stored at a data center and maintained by a cloud computing services provider.
This also means that the location of the hardware‚ the operating system which it runs on‚ and the server‚ is not important to the user. That was why the concept of the “cloud” was borrowed from old telecoms network schematics where the location didn't matter‚ and the public telephone network was simply represented as a cloud of stuff.
This is unlike what was obtainable in the past where users had to create and save files in a physical hard drive‚ floppy disks‚ or USB drives‚ and without those hardware components‚ the data was inaccessible.
What is the History of Cloud Computing?

The concept of cloud computing can be traced back to the 1960s‚ and to an American computer scientist‚ J.C.R. Licklider.
Licklider envisioned a world where everybody was connected by way of computers and everyone could access data and every other program irrespective of the location of the access point.
This vision‚ the “Intergalactic Computer Network”‚ widely known as the “predecessor of the internet”‚ was what led to the birth of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET). This was the first network that allowed computers to share digital files even when they were not physically in the same location.
The term “cloud computing”‚ however‚ was coined in 1997 by Professor Ramnath Chellappa of Emory University‚ Goizueta Business School.
He was the first person to define cloud computing while delivering a talk on “The new computing paradigm”. He defined it as a new “computing paradigm‚ where the boundaries of computing will be determined by economic rationale‚ rather than technical limits alone.”
Cloud Computing in Recent Years
Cloud computing began to gain popularity in the 90s when more companies started understanding how useful it is and the services that can be rendered with it.
The most popular company to adopt cloud computing successfully back then was Salesforce.
In 1999‚ Salesforce pioneered the concept of delivering software programs to end-users via the internet. Any end-user with internet access could then access and download these software programs. This meant that without leaving the office‚ companies could buy only the software they needed in a cost-effective manner.
By the early 2000s‚ Amazon launched its web-based retail services. They equally launched the Amazon Web Services‚ the Infrastructure as a Service arm of Amazon‚ in 2006. And with the launch‚ the company started offering online services to other companies like Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)‚ and Amazon Mechanical Turk‚ which provides a lot of cloud-based services like computation‚ human intelligence‚ and of course‚ storage.
That same year‚ Google launched Google Docs‚ which is compatible with Microsoft Word‚ and Google Spreadsheets which is compatible with Microsoft Excel.
With Google Docs‚ users can create‚ edit‚ and save documents in the cloud. And with Google Spreadsheets‚ they can create‚ edit‚ and update spreadsheets‚ and equally‚ share the data online. And in 2012‚ they launched Google Drive.
Soon enough‚ other major players like Microsoft (Azure)‚ and Apple (iCloud) started hosting the cloud and selling end-users the rights to store data on their networks and to use their clouds. And with time‚ they started creating ecosystems that can communicate between programs and devices. A good instance is how a song is automatically synced to the iTunes software on an iPhone as soon as it gets downloaded.
How Does Cloud Computing work?
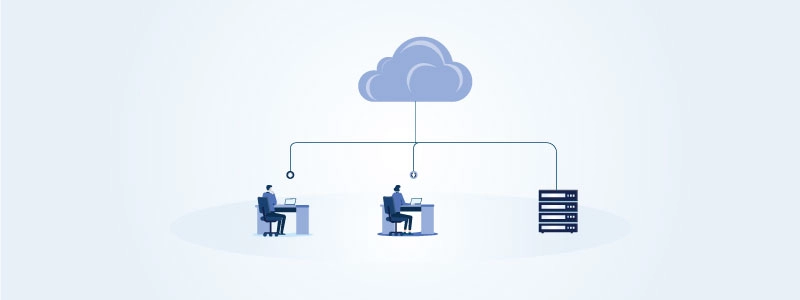
To understand how cloud computing works‚ you have to first understand the cloud computing infrastructure.
First‚ we will start with the concept of “the cloud”.
The cloud basically means a decentralized place where satellite networks are used to share information. It is a metaphor for the internet.
Every application in the cloud is hosted by a company‚ and that company has the responsibility of maintaining the massive data centers where the information sent by users to the cloud is hosted.
Many cloud computing services have different modes of operation. However‚ they basically all have browser-based dashboards where the resources needed to work with cloud services are provided. Through these cloud computing dashboards‚ clients can get easy access to databases‚ servers‚ storage‚ and other application services they need over the internet.
To take it further‚ we are going to divide cloud computing into two sections:
- The front end and
- The back end.
 The Front End
The Front End
The front end includes computer networks‚ computers‚ smartphones‚ tablets‚ applications‚ and every other thing that helps a user to access the cloud computing system. It is the section of cloud computing where a client can access the data stored in the cloud through the use of cloud computing software or an internet browser.
 The Back End
The Back End
The back end is the primary component of cloud computing. It includes servers‚ databases‚ central servers‚ data storage systems‚ programs‚ and every other component that helps to securely store data and information and executes all requests made by a client.
The central server‚ on the other hand‚ uses software known as “middleware” to ensure that the connectivity between the devices linked through cloud computing is seamless. It facilitates operations by following protocols‚ which are just a set of rules.
Through the back end‚ cloud computing service providers do their best to prevent data breaches‚ data losses and reduce security threats by maintaining multiple copies of the data that users store in the front end.
What is Cloud Computing Used For?
As technology advances‚ different individuals and companies now use cloud computing for the smooth functioning of their businesses‚ and for several other reasons.
For many companies‚ cloud computing is now an indispensable tool for communication and collaboration across distributed teams. From Google Cloud to Azure and even Amazon Web Services‚ many companies are adopting cloud computing to optimize resources‚ increase flexibility‚ and most importantly‚ reduce cost.
The potential uses of cloud computing are only starting to get adopted‚ and based on the vast possibilities that can be realized from it‚ it is going to change the way we do business and life‚ in the long run.
In the next few pages‚ I am going to examine five uses of cloud computing and what they can help you do. And I am pretty sure that by the time we are done‚ you are most likely going to become a fan of cloud computing whether you are an individual or you represent a company.
Five uses of cloud computing
 Entertainment
Entertainment
Apart from its efficiency and flexibility‚ one thing that makes cloud computing very beneficial is its scalability. Today‚ a combination of highly improved internet speed and media streaming industry giants like Spotify‚ Tidal‚ Hulu‚ and Netflix are dominating the entertainment industry by employing cloud computing processes.
Netflix alone has an enormous database of movies that are available for their consumers in the cloud. After migrating its database to the cloud in the company has been able to onboard more customers‚ produce more content‚ reduce storage amount in real-time‚ and easily handle sharp usage spikes that occur when new episodes are made available.
Apart from that‚ cloud computing functions vitally in the online gaming world too. A lot of online games are now enjoying a smooth and instant connecting experience which is only made possible through cloud computing.
With the high processing power the cloud is known for‚ video games can now run games on remote servers and stream the games to a player's device directly. This process‚ referred to as cloud gaming or gaming-as-a-service‚ shifts the weight of the processing from the devices to the cloud and allows players to play without downloading the games to their consoles or devices.
 Big data analytics
Big data analytics
Before the advent of cloud computing‚ employing the use of big data to study patterns and insights was both a very expensive and overwhelming process. Cloud computing changed that by offering a lot of solutions for big data analytics.
First of all‚ by the use of cloud computing‚ companies no longer need to use their in-house development resources when they want to compile and analyze data.
Instead‚ they can collect as much data from all the sources available to them‚ connect the data to the cloud‚ analyze them‚ and glean insights in real-time. This benefit can help you make business decisions quickly.
Secondly‚ cloud platforms offer unlimited storage to users so they can gather insights like sensor data‚ search and site navigation routes‚ customer shopping habits‚ etc.
This means that even if you are not ready to do anything with the data‚ you can gather them and store them for later use since the storage capacity is unlimited.
Moreso‚ with the incept of the cloud‚ companies can now use tools like data lakes‚ data warehousing‚ and extract‚ transform‚ and load (ETL) to store and process both their structured and unstructured data.
Lastly‚ cloud computing has a lot of offerings for machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) that can help you generate business value from a large quantity of data by finding patterns in your data.
The insights you get from these data can help with equipment and cost optimization‚ marketing and customer experience improvement‚ and above all‚ drive business growth.
 Communication
Communication
Cloud computing provides video-conferencing application services in the cloud through which you can host meetings‚ share your screen‚ and even make presentations smoothly.
Applications like Zoom and Skype‚ plus the entire Google Suite of applications like Google Meet and Calendar are all cloud-based. These applications help people and businesses to collaborate and communicate on a global scale.
In addition to that‚ social media applications like Whatsapp‚ Twitter‚ Facebook‚ and Linkedin all make use of cloud computing to connect users so they can share videos‚ stories‚ experiences‚ and images‚ on a real-time basis.
 Data backup and disaster recovery
Data backup and disaster recovery
Cloud computing provides a solution to the problem of data loss and recovery. Many computer owners have experienced the pain and stress that comes with losing valuable files stored on physical hard drives. But with cloud computing‚ you can easily have accessible backup solutions to keep your files safe whether they are family photos‚ term papers‚ or company files.
Cloud computing also makes disaster recovery cost-effective and very fast. You can prevent a disaster in one of your data centers by simply turning to a different data center. And it is so easy‚ that all you have to do is to pick the backup you wish to restore and click a button.
 Data storage
Data storage
Cloud computing enables you to store your files securely in the cloud as a backup in case there is a fire breakout‚ equipment malfunction‚ ransomware attack‚ or natural disaster.
In addition‚ storing your data in the cloud will make them accessible everywhere in the world to whomever you wish. This aspect of cloud computing has proven to be very helpful to most organizations since the Covid-19 pandemic‚ as a lot of workers now have to work from home. This way‚ despite the lockdown of 2020‚ many global offices could still coordinate their staff across different locations.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing?
In this section‚ I will be sharing the pros and cons of cloud computing with you.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
 Competitive Edge
Competitive Edge
With cloud computing‚ you have a strategic edge over competitors. This is because you can access recent apps without spending money and time on installations.
 Data Backup and Restore
Data Backup and Restore
As soon as your data is online‚ you can easily backup and recover it. If you were using an on-premise system‚ this process would consume a lot of time.
 High Speed
High Speed
With a few clicks‚ you can quickly deploy the service. This allows you to access the resources you need within a short time.
 Unlimited Storage
Unlimited Storage
Cloud computing offers large storage space with the ability to expand when needed. You only need to pay a little monthly or annual fee to enjoy unlimited storage‚ depending on your service provider.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing equally comes with its downsides. Some of the risks of cloud computing are:
 Security risks
Security risks
One of the major disadvantages of using cloud services is the security risks involved. Cloud computing basically means you are sharing your company's sensitive information with a cloud service provider who is a third party. This information could be accessed by hackers.
 Internet connectivity
Internet connectivity
No matter how good your cloud computing provider's services are‚ your ability to make the most of the service and access your data is dependent on how good your internet connectivity is. If the internet is experiencing downtime‚ your business operations will likely grind to a halt.
 Varying Performance
Varying Performance
When working online‚ the apps run on a server that provides resources simultaneously to other companies. If there is a DDOS attack or greedy behavior on one of the tenants of the server‚ your performance will reduce greatly.
 Limited control
Limited control
As a cloud user‚ you have little or no control over a cloud infrastructure. The cloud service provider owns‚ manages‚ and monitors it directly and the most you can do is manage the data and applications operated on the cloud‚ but you won't be able to access the server shell or perform other key administrative tasks.
 Technical issues
Technical issues
Just like any other IT setup‚ your cloud service provider could face a power outage or have other service maintenance issues like reboots. Despite having high maintenance standards‚ even the most efficient service provider faces these kinds of issues from time to time. This could make you experience downtime and incapacitate your business operations.
 Low Bandwidth
Low Bandwidth
Some service providers limit the bandwidth usage of users. So‚ if your company surpasses the allowance‚ the extra charges may be expensive.
 Vendor lock-in
Vendor lock-in
Moving from one vendor to the other can prove to be a herculean task. This is a huge disadvantage of cloud computing. Different vendors operate on different platforms‚ and it may not be easy to move from one cloud to the other.
Difference between Cloud Computing and Traditional Computing
The differences between cloud computing and traditional computing are as follows:
1. Position
Cloud is the first difference between traditional and cloud computing. Cloud computing works on servers that are facilitated by external hosts. Traditional computing takes place on physical hard drives and website servers.
2. Architecture
The architecture of any computing enables you to understand the design of the application. Cloud computing apps are based on infrastructure development. They utilize theories of user interface and automation.
Traditional apps consist of 3 essential levels:
- Database
- Presentation‚ and
- Logic
3. Expenses
Traditional computing costs more than cloud computing. This is because unlike in traditional computing‚ the task of operating and maintaining the cloud server is taken up by the cloud provider. This means that companies can save more by not purchasing costly equipment.
4. Availability
Cloud computing offers improved highlights and customary updates‚ which enables users to maintain their businesses in a cost-effective manner. Even if you encounter any problem‚ it can be fixed within a short time.
Traditional applications require manual scripting‚ and if something goes wrong‚ a programmer will need to go through all the lines of codes before deploying the software.
5. Security
This is a critical aspect of maintaining a business‚ and both cloud and traditional computing have concerns about security. Cloud servers have several security layers but they are not cyberattack-proof. Hackers can access the server and steal information the same way they can access on-premise software.
What makes up a cloud computing system?
A cloud computing system is made of platforms such as the back end‚ front end‚ and mode of delivery that the network uses. The main components are SaaS‚ PaaS‚ and IaaS‚ which we will discuss subsequently discussed. However‚ there are other categories that make up the architecture of cloud computing.
1. Database-as-a-Service
It works like the physical database only that this component is live and functions remotely. The main objective of the service is to provide cheaper database services using different hardware and software.
2. Storage-as-a-Service
As the name implies‚ it is the component for storage‚ also known as “on-demand disk space”. Other components use this service as their base component.
3. Information-as-a-Service
This component enables users to access information from anywhere. The information is fetched remotely. It may include online news‚ validation of credit cards‚ internet banking‚ real-time prices of stocks‚ etc.
4. Application-as-a-Service
This is the already built application that end-users can utilize when they connect to the internet. Examples of applications are Google calendar‚ Gmail‚ and Salesforce.
5. Process-as-a-Service
This component is a combination of different resources like services and data. It can be hosted remotely or within similar cloud-computing resources. It is majorly used for business processes that require the combination of information and key services to formulate a process. An example of this component is a mobile network where users need the service provider to send internet settings as an SMS to activate the network.
6. Platform-as-a-Service
This component enables the development of applications. This is where the database is created‚ implemented‚ tested‚ and stored. It also enables the development of enterprise-based applications.
7. Integration-as-a-Service
Here‚ an already built application is integrated with several other applications. Hence‚ it serves as a mediator between local machines and remote servers. It fetches stacks from the cloud and communicates with the local machines. An example of this service is the integration of Google maps in salesforce.
8. Security-as-a-Service
Many customers need this service because we cannot talk about cloud computing without expressing concerns about data security. Anyone who decides to use a cloud-based service needs security as all operations and data are remotely handled.
9. Management-as-a-Service
This component helps in managing the entire cloud environment‚ including downtimes‚ virtualization‚ and utilization of resources.
10. Testing-as-a-Service
This service enables the remote testing of applications. It helps the programmer to check the requirement for designing a database for the app as well as the required security features.
11. Infrastructure-as-a-Service
This component comprises the networking‚ servicers‚ software‚ and hardware that are completely virtual. It serves as the basis for purchasing and processing all resources in the cloud. When you purchase software online‚ you can't see the process but everything is happening at the backend. Infrastructure-as-a-Service is the component that puts all the pieces together.
Why is Cloud Computing so important?
Most people use a plethora of cloud services even though they don't realize it. Google Drive‚ Facebook‚ Instagram‚ Gmail‚ and iCloud‚ are all cloud-based applications where users send their personal data to cloud-hosted servers where the information is stored for later use.
Cloud computing is even more important for businesses as a lot of businesses need to access a huge amount of data over a secure network on a daily basis.
Benefits of Cloud Computing

Cloud computing is vital in ensuring the progress of the world we live in today. It is notably important for many reasons. Chief among them is that it helps businesses save costs‚ but apart from that‚ it has several other benefits for businesses which is why millions of businesses are using it.
Below‚ I am going to share nine benefits of cloud computing with you.
 Business continuity
Business continuity
Nothing grinds a business to a halt more than a disruption. From ransomware attacks to natural disasters‚ if it hits‚ most businesses could lose their data if it is not backed up in the clouds. And without cloud computing‚ it would be impossible for employees to access valuable data that will ensure that the business continues to run.
A good case study is the Covid-19 pandemic of 2020. The demand for the real-time applications of cloud computing accelerated in recent times‚ especially when the global Covid-19 pandemic broke out‚ as most companies had to employ innovative strategies to avoid stagnation and ensure business continuity.
Businesses that were employing cloud computing services allowed their staff to start working from home. They continued operation in real-time in spite of the disruptions that were taking place globally.
 Security
Security
According to RapidScale‚ 94% of businesses saw an improvement in security after implementing cloud solutions. Also‚ 57% of companies using cloud solutions said it provided them with better data security. This amped-up security is possible because the data that is stored in these databases and transmitted over networks is encrypted‚ making it difficult for hackers or any unauthorized person to access the stored data.
This level of security associated with cloud hosting of data files and software programs minimizes the threat of cybercrime. And even if a computer is damaged or compromised by a virus‚ the company can still access its data with another device without the fear of losing sensitive data‚ as every document is saved in the cloud.
In addition to that‚ cloud computing makes it more difficult for bad elements to steal. Some cloud computing hosting providers go as far as offering firms secure portals that consist of comprehensive encryption and login security systems which makes it almost impossible for anyone to steal stored data.
 Reduced Cost of Operation
Reduced Cost of Operation
Owning and maintaining a data center that will support all your business needs is very costly. It will require the hiring of staff‚ running of upgrades and regular maintenance‚ and development of in-house solutions.
Every business would jump at the opportunity to minimize costs‚ and cloud computing provides that option.
Transitioning to cloud-based services reduces the costs of maintaining and managing IT systems as you do not have to buy expensive equipment and systems for your company.
Other costs that will reduce include:
- Energy costs
- Costs of upgrading new software and hardware
- Cost of hiring expert staff to handle certain IT tasks
- Fewer downtimes
With the pay-as-you-go option that cloud computing comes with‚ businesses can efficiently optimize their budget and use only the services they need to grow‚ develop and remain competitive without having to spend so much.
With cloud computing‚ you are only required to pay subscription fees for the services you are using. And if you wish to stop using a particular service‚ you simply stop paying for it.
 Ease of access
Ease of access
With cloud computing‚ you have easier access to company documents‚ software‚ and backend files. Your employees can work remotely. All they will need is a device with internet access and the right security protocols. With that‚ everyone can access relevant files remotely‚ and work easily‚ as the whole company is connected in the cloud.
 Access to automatic updates
Access to automatic updates
Many cloud computing service providers include automatic updates in your service fees. When you subscribe to their service‚ your system will be updated regularly with the latest technology including upgrades to servers‚ up-to-date software versions‚ and computing power.
 Scalability
Scalability
Cloud computing allows you to quickly scale operations and storage needs as desired‚ giving you room to stay flexible. You do not need to purchase and install any expensive upgrades by yourself. Even if you want to downgrade‚ the service provider handles everything for you on demand.
 Data backups and recovery
Data backups and recovery
One of the most important reasons why we need cloud computing today is the option of data backup.
With cloud-based services‚ you can store your business data in the cloud which has an integrated data backup and recovery process.
This process keeps your data secured and protected from all emergency scenarios ranging from power outages to natural disasters‚ physical theft‚ and cyber attacks. And in case of a disaster‚ you can easily recover your data just by the click of a button‚ and resume operations at a moment's notice.
When data is stored in the cloud‚ the cloud service provider splits it into encrypted fragments and proceeds to distribute it across different remote data centers. This way‚ even if a problem is encountered in one of their servers‚ your data will remain safe as another copy is equally saved in another location. And if a cybercriminal succeeds in stealing your data from one location‚ it will be useless.
 Mobility
Mobility
According to a Statista report‚ over 6.3 billion people use smartphones globally. Cloud computing gives users the ability to access corporate data using their smartphones‚ thereby ensuring that nobody is left out. Employees who don't live close to the office can keep up to date with their co-workers and clients because of this benefit.
Through this cloud computing feature‚ information can be shared with freelancers‚ remote employees in a different geographic location‚ and staff who work from home due to Covid-19 restrictions.
 Collaboration Efficiency
Collaboration Efficiency
Unlike traditional methods of collaboration‚ cloud computing enables you to communicate with team members across the globe in real-time. You do not need to be in the same location with your employees or contractors as everyone involved in a particular project can access the same file through the cloud.
What are the types of cloud computing?
Cloud computing can be divided into four main categories which are:
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
- Community cloud
I am going to discuss them in detail below‚ talk about the benefits of using each type‚ and also talk about their downsides.
 Public cloud
Public cloud
In this type of cloud computing, the basic computing resources including the memory, storage, central processing unit (CPU), and network are hosted in one of the data centers managed by the cloud service provider. Public clouds are usually scalable because they come with lots of available space.
The public cloud service providers also offer managed services like security systems, applications, and database servers which you can rent if you don't want to save the cost that comes from the setup and management of the whole solution. And to access your resources, all you need is a device with a web browser and internet access.
The leading companies offering public cloud services are:
- Microsoft Azure
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)‚ and
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Benefits of using public cloud
1. Reduced capital expenditure
In the public cloud‚ the hardware is owned‚ hosted‚ and maintained by the cloud service providers. Customers don't have to buy or maintain any of the hardware that makes up their public cloud IT infrastructure.
This type of cloud computing comes with a pay-as-you-go payment structure that gives consumers the ability to only pay for what they consume. And with this payment structure‚ customers can scale the size of their solution so it can accommodate their usage peaks and troughs‚ saving them a lot of money and giving them more flexibility.
2. Security and data recovery
Public cloud vendors invest 10s of billions of dollars in their data centers for storage facilities‚ state-of-the-art fault-tolerant power supplies‚ and automated monitoring and maintenance systems.
By using the public cloud‚ you get to enjoy these‚ plus your vendor's disaster recovery plan and security. This way‚ not only is your data secure‚ but even if a disaster were to occur‚ your system will keep running because of the built-in redundancies.
Disadvantages of using public cloud
1. Lack of control
The main disadvantage of using the public cloud is that the operating system and IT infrastructure here are under the full control of the cloud service provider. If the vendor makes a significant change in their business model‚ or worst still‚ goes out of business‚ you will have no choice but to start making infrastructure changes on short notice.
2. Security risks
Another disadvantage of using the public cloud is that there is the risk of vulnerability in the cloud architecture that comes from having unpatched security. If left unchecked‚ this vulnerability can expose your company to unnecessary risks.
 Private cloud
Private cloud
Unlike the public cloud‚ private clouds are owned and utilized by single organizations. These customers get dedicated infrastructure not shared with anyone else. And in the same way‚ the organization involved bears the cost alone.
The cloud service provider does not provide any cloud management service here‚ instead‚ the maintenance of the private cloud is done by the user.
Advantages of private cloud
1. Tight security
Private cloud comes with tight security regulations. It is easy to restrict access to your valuable assets with the use of the private cloud. Moreover‚ you can easily move your data‚ programs‚ and applications wherever you want‚ whenever you want.
2. Control
With the private cloud‚ you can control the environment. You can design your cloud computing approach to meet your internal processes and internal preferences. And there is no risk of getting your company's infrastructure disrupted by any sudden change since you control the cloud and not an outside vendor.
Disadvantages of private cloud
1. High maintenance cost
Although there are lots of benefits that come from using a private cloud‚ they come at a high cost. The company that owns the private cloud hosts and maintains the software and hardware‚ and it is not cheap.
2. Lack of versatility
Private clouds do not have the kind of versatility associated with public clouds. It is difficult to scale operations quickly in a private cloud. Here‚ before any expansion occurs‚ more hardware and storage capacity has to be added to the system‚ which means more cost too.
 Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines private and public clouds. The two platforms are designed to interact with each other and allow applications and data to move seamlessly to and from each other.
If a company needs a little bit of public cloud and a little bit of private cloud‚ the hybrid cloud option is its best bet. For instance‚ with a hybrid cloud‚ an organization can process their data on their premises‚ and still‚ use the almost unlimited storage capacity that the public cloud offers.
This model is usually employed by organizations whose on-site infrastructure needs to scale so as to meet their fluctuating business demands. This way‚ they can enjoy the processing power that comes from using the public cloud while enjoying the control that comes from keeping their sensitive data on their private cloud.
Advantages of hybrid cloud computing
1. Best of both worlds
The main advantage here is that a hybrid cloud solution offers businesses the best of both worlds.
This cloud computing type gives you the control and security that comes with using a private cloud and still provides you with the scalable computing power that public clouds offer. This means you can increase your compute capacity even though you are still using the on-premise resources you paid for.
Also‚ companies can safely store their data behind the encryption protocols and firewalls of the private cloud and still move their data to a public cloud environment whenever required.
Disadvantages of hybrid cloud
Communicating and sharing data between a public and private server comes with a potential security and performance risk. To mitigate this‚ you must ensure that your cloud service provider is knowledgeable and very experienced with the hybrid cloud computing model
 Community cloud
Community cloud
A community cloud is essentially a private cloud that functions as a public cloud. Its infrastructure is designed to be used exclusively by a specific community of users from organizations who want to share the same applications.
These users‚ although in different organizations‚ operate within the same industry‚ and concerns like compliance‚ security‚ and performance are common to them. This model is mainly used by financial service firms‚ healthcare organizations‚ government agencies‚ and other professional bodies.
Advantages of community cloud
1. Industry compliance
Organizations that make use of this cloud computing model usually have common security needs. Because of this‚ monitoring of industry regulations is done collaboratively by all the users‚ and any decisions made to effect changes to the system are made in the best interests of all the group members.
2. Flexibility
Even though community cloud comes with a shared space‚ the system is still very flexible. Each individual organization can still set access controls and adjust the system to meet the demands of their own organization.
Disadvantages of community cloud
1. Performance and prioritization issues
Since the cloud is shared across organizations‚ servers would have to adjust to different demands by the organizations using the shared storage‚ and this can lead to performance and prioritization issues.
Characteristics of cloud computing
The flexibility that comes with cloud services‚ coupled with the ever-growing techniques and set of tools that it comes with has made it to get deployed quickly across many industries. In this section‚ I am going to share some of its essential characteristics.
1. On-demand self-service
This is one of the most essential characteristics of Cloud Computing. This feature enables consumers to monitor the computing potentialities like server uptime and allotted network storage constantly and control the computing abilities based on their needs‚ without having to interact with each individual cloud service provider.
2. Easy to maintain
Cloud computing resources are regularly updated so their potentials can be fully optimized. Once updated‚ the devices will start performing faster. So if you use the cloud‚ you wouldn't need to bother about the servers because they don't require much effort to maintain‚ and the downtime is either zero or very low.
3. Resources pooling
This simply means that the computing resources of a cloud service provider are shared to serve an aggregate of consumers‚ providing every one of them with virtual and physical resources allotted and re-allocated dynamically according to the individual requirements of each consumer.
A multi-client pattern is employed for processing services‚ data storage services‚ and overall network bandwidth provision services. The cloud service provider allocates these resources in real-time without conflicting with the client's experience.
4. Security
Cloud services create multiple copies of stored data to prevent the data from getting lost. And if anything happens to any of the servers and it loses the stored data somehow‚ the copied versions will be restored to the other servers where they were saved. This way even if a file gets corrupted suddenly‚ the data is still secure as the copied version will get restored.
5. Measured and reported service
Cloud computing systems give both consumers and providers the ability to measure and report the services that are getting used and the purpose for which they are used. This feature makes for efficient monitoring and billing for resources like storage‚ bandwidth‚ memory‚ and processing‚ and ensures that these resources are used optimally.
6. Economical
Cloud computing helps organizations to reduce what they would have spent on IT infrastructure as all they have to pay for is the administration space that they use. Most cloud services are on a pay-as-you-go basis‚ so organizations don't need to spend a lot of their budget on IT infrastructure as the cloud service provider maintains it for them.
7. Rapid scalability
Cloud computing can be scaled rapidly which makes it possible for workloads that need a lot of servers to be run effectively at a reduced cost for short periods.
8. Resilience
Cloud computing offers organizations the ability to recover quickly from disruptions. In the case of damage or a disaster‚ the servers‚ network systems‚ and databases can restart and recover very fast‚ thereby preventing any form of disruption for an organization.
9. Availability
Cloud services can be remotely accessed. This means that users can access and utilize cloud resources anywhere they are with no geographic limitation or restriction. All they need is a device like a laptop‚ a smartphone‚ a tablet‚ and an internet connection.
What cloud computing services are available?
There are three types of cloud computing services‚ and they are:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
These three can also be referred to as the cloud computing stack as they build on top of each other. In other words‚ SaaS is built on PaaS‚ and PaaS is built on IaaS.
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS in cloud computing simply means a fully developed software solution that is ready to be bought and used on a subscription basis over the internet to meet a wide variety of business needs like market automation‚ customer relationship management (CRM)‚ or business analytics.
It is the most common form of cloud computing service. Most people use it every day even though they don't understand it.
Although some SaaS programs are free‚ many of them require that you make an annual or a monthly subscription before you can use the service.
Once you subscribe to a SaaS service‚ the service provider has the responsibility of managing the operating systems‚ the middleware‚ the infrastructure‚ and the data that is needed to deliver the program‚ making sure that the software is available for customers wherever and whenever they need it.
Most SaaS applications do not require downloads‚ installations‚ or management‚ as they are run directly on web browsers. This allows organizations to streamline their operations with multi-cloud and hybrid deployments‚ as software management issues are greatly reduced for the internal IT teams.
Examples of SaaS solutions are
- Google Docs
- Salesforce
- Microsoft Office 365
- Cisco WebEx
- Dropbox‚ etc
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) has to do with the supply of the tools needed to develop‚ test‚ deliver‚ and manage software applications. It provides computing and storage infrastructure‚ plus a development platform layer that contains database management systems‚ web servers‚ and software development kits (SDKs).
Companies that develop web-based applications‚ mobile apps‚ and software find it very helpful because setting up the underlying infrastructure of servers‚ purchasing the storage‚ network‚ and databases that they will need for development can be very expensive. But by using Platform as a Service‚ these companies can get access to the development tools they need when they need them‚ without having to buy them outrightly.
Moreover‚ by using PaaS tools that have extensive pre-coded applications‚ companies can spend less time coding‚ which means they can develop their products and bring them to the market faster.
Examples of PaaS solutions are
- Microsoft Azure
- Google App Engine
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Apache Stratos
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides users the ability to purchase‚ install‚ configure and manage operating systems‚ business analytics‚ applications‚ middleware‚ development tools‚ and any other software they need to use. Through it‚ users gain access to basic computing resources like data storage capacity‚ processing power‚ servers‚ and hardware in the cloud without a need for large physical infrastructure on the ground.
An IaaS provider manages the physical end of these infrastructures (like the data storage space‚ and servers) in a data center while allowing customers to customize the virtual resources to meet their required needs.
The provider also has the responsibility of updating their system continuously with the latest patches‚ making it easier for a company to run new applications and programs. This way‚ the IT department can focus on core business functionalities and not spend all their time troubleshooting and managing the infrastructure.
It is the most flexible and comprehensive type of cloud computing service available‚ and the fundamental platform for the building of new technologies.
Examples of IaaS solutions are
- Amazon EC2
- Digital Ocean
- Google Compute Engine
What are examples of cloud computing?
There are so many cloud computing examples that are worth mentioning. But for the purpose of this guide‚ I am going to group them into five broad categories.
- Data storage
- Healthcare
- Government
- Marketing
- Education
1. Examples of Cloud Computing in Data Storage
Cloud storage service is a very vital solution for businesses because they need to store files and back up their data easily. There are a lot of cloud storage providers today and the numbers keep increasing each day.
Some examples of cloud storage are:
- Dropbox
- Google Drive
- One Drive
Cloud storage providers like Dropbox give their users as much as 1 terabyte free storage for their files. Google Drive‚ on the other hand‚ gives users up to 15 gigabytes of free storage space‚ while One Drive gives 5 gigabytes.
Facebook and Instagram are also examples of cloud computing in data storage. Just like other social media platforms‚ they allow users to store an unlimited amount of images‚ videos‚ and other information on their profiles and pages. More so‚ people can exchange data by sending private messages on these platforms too.
2. Examples of cloud computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing in healthcare can be applied in public and personal health care‚ bioinformatics‚ telemedicine‚ and e-health services.
Examples of cloud computing in health care are
- IBM Cloud
- Dell's Secure Healthcare Cloud
- ClearDATA
Doctors‚ nurses‚ and other medical professionals use cloud computing to host information‚ share and analyze it‚ and remotely perform diagnostics.
Through this fast sharing of information‚ doctors can save costs‚ conveniently access their patients' medical information anywhere in the world‚ and are able to quickly make prescriptions. This makes it possible for them to give their patients the best possible care with little or no delay‚ making them more efficient in their delivery.
Although many hospitals haven't adopted cloud computing in their delivery system‚ future forecasts predict that there will be a massive adoption of cloud solutions in the health care sector.
3. Examples of cloud computing in Government
Many governments are starting to adopt cloud computing in their operations. A good example is the United States government which instituted the U.S Federal Cloud Computing Strategy under the Obama administration‚ to accelerate the adoption of cloud services across all departments.
With this‚ citizens can enjoy e-governance services as they can conveniently handle large transactions and reduce congestion bottlenecks. The government on the other hand enjoys the use of standardized software‚ enhanced security‚ improved collaboration‚ and a reduced need for computing hardware.
Some examples of cloud services in government are
- IBM SmartCloud for Government
- Salesforce Government Cloud
- Microsoft Office 365 Government and Azure Government
- Huddle
4. Examples of Cloud Computing in Business and Marketing
Marketing is an essential part of any business that wants to remain profitable‚ and it involves the processing and analysis of large information. Marketers need this information to determine the inbound or outbound strategy to deploy‚ they need it to promote products to a target audience‚ they need it for better customer communication and effective market segmentation too.
In essence‚ today's businesses need cloud services to access a secure environment where they can get real-time information about their prospects and customers.
This information has become essential as effective marketing now demands personalization.
Customers want communication to be more human and that can only be made possible through cloud computing. Through it‚ marketers can manage a large database‚ access client information with precision and speed‚ and personalize their strategy.
Some examples of cloud solutions in business and marketing are
- Salesforce
- Tableau
- Quantcast
- Redislab
- PowerBi
- MLab
- NoSQL
5. Examples of Cloud Computing in Education
Education has evolved greatly in the past few decades. There are almost as much online classes as there are offline classes today. There is a multi-million audience interested in getting knowledge online. Such a wide audience will need a significant amount of technical resources from servers‚ and lots of hardware and software to be able to provide them with video lectures and other educational materials.
Cloud computing provides the following solutions for academic organizations and schools
1. Provision of Learning Management Systems and other eLearning solutions
2. Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solution which gives both students and instructors access to teaching and learning software.
3. Storage and display of tutorials and lectures through video hosting cloud solutions.
4. Ability to access experimental data for research purposes.
Examples of cloud services in Education are
- Amazon Web Services
- Coursera
- Google Classroom
- Ratatype
Who is using Cloud Computing?
According to Gartner‚ the revenue forecast for global public cloud services in 2024 is $331 billion. Many companies are starting to embrace cloud services‚ especially since the lockdown of 2021. But apart from that‚ other benefits like data storage and management‚ prevention of security leaks‚ and predictive analytics has made it even more enticing.
It will be nearly impossible to list all the companies currently using cloud computing in their operations.
But here are 10 top companies using and benefiting greatly from cloud computing.
 Apple
Apple
Apple users exchange apps and data using the cloud‚ and they make upgrades without having to physically modify their hardware or software.
Apart from that‚ most people use iCloud‚ Apple's cloud program. And in addition‚ Siri‚ the Apple product that revolutionized smartphone technology‚ receives and processes inquiries with the cloud before responding to them.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
Pinterest is a very popular social networking site‚ and they have been utilizing cloud computing since inception. Currently valued at over $12 billion‚ the platform serves as an online pinboard for storing different boards and collections. But much more than that‚ it helps bloggers and marketers generate traffic massively too.
Through cloud computing‚ Pinterest grew at a tremendous rate‚ handling heavy amounts of traffic and data to the point that it has become the 14th largest social media platform in the world with 459 million active monthly users‚ according to Hootsuite.
 Netflix
Netflix
Netflix began as a DVD rental business‚ but from there‚ it has grown to become a streaming entertainment giant with about 53.5% of the global streaming market according to a 2020 Statista survey. The company commands the attention of tens of millions of people eager to watch its critically acclaimed programs‚ latest box office releases‚ documentaries‚ and original series.
Due to its large user base‚ Netflix had to find a way to store its data. It needed the right computing capabilities and infrastructure that allows quick scaling‚ as using an in-house data center was proving to become inefficient.
Even though cloud computing was a relatively new technology‚ the streaming giant adopted the technology and moved their data to the cloud. With AWS‚ they now provide steady and secure service to their over 192.95 million global subscribers in over 190 countries and in over 30 different languages.
 eBay
eBay
eBay is one of the leading e-commerce platforms in the world‚ with over 175 million active buyers worldwide.
With over one billion live listings at each given time‚ it needed to adopt cloud technologies to be able to keep managing its data and providing secure transactions for its users. And in 2018‚ eBay relocated its marketplace to Google's cloud platform. The project was completed in a record time of five months with the aid of a team of engineers. Later in the same year‚ they started experimenting with machine learning algorithms to help with identifying pictures on Google's cloud platform. And in four days‚ they were able to run the tests with Google Cloud.
 Paypal
Paypal
Paypal is one of the leading FinTech platforms for receiving and making online payments. As at the second quarter of 2021‚ the FinTech giant had processed over 3.74 billion transactions worth more than 311 billion dollars‚ and was serving over 300 million users worldwide.
To be able to manage the sheer volume of transactions they handle and still prevent fraud and maintain top security‚ they had to partner with Google Cloud and start using cloud computing technology in 2018.
 Capital One
Capital One
Capital one made a unique move by transferring its complete infrastructure from its data centers to AWS‚ opting to employ a public cloud instead of a private cloud like many companies would. The company still uses other cloud service providers‚ but AWS is its main supplier.
 Kroger
Kroger
Dating back to a few centuries ago‚ Kroger is one of the leading American retail companies. And with some innovative technologies like smart pricing and digital shelf technology‚ Kroger is changing the way grocery shopping is done.
With the aid of cloud computing‚ the grocery store chain is now able to use machine learning and AI to develop new products while developing secure solutions for e-commerce at the same time. Kroger distributes its cloud fees which runs into millions of dollars between Microsoft Azure and Google.
 Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola
During the Super Bowl of 2014‚ the Coca-Cola company experienced a splurge in traffic that made it move its data to the public cloud. With this move‚ the company was able to introduce automation which helped them to improve their performance‚ reduce their operational costs and save about 40% of their operational budget‚ and increase their operational capabilities.
The beverage giant is one of Amazon's largest customers today.
 Fitbit
Fitbit
Fitbit is one of the leading smartwatch manufacturing companies in the world. In order to re-energize the brand and appeal to a broader audience‚ the company started collaborating with Google For Healthcare‚ allowing users to share their health data with doctors and other healthcare professionals. This way‚ doctors can work efficiently with patients‚ plan their visits‚ and monitor them remotely.
 Gameloft
Gameloft
Gameloft is a video and mobile game development company based in France and founded in 1999 with the goal of producing quality games that can be easily downloaded to mobile phones. The kind of service they provide requires a well-managed infrastructure to ensure that even when new games are launched and the servers experience high traffic spikes‚ there will be zero downtime. To do this with their own data centers proved to be too costly so the company moved their game servers to the cloud and improved the user experience for gamers.
What are some challenges of Cloud Computing?
1. Security
This is usually a top concern for investors in cloud services because your data is stored by an external vendor that you can't see. Whenever you get information about compromised credentials‚ broken authentication‚ data breaches‚ or account hacking in an organization‚ it gets you worked up.
Thankfully‚ cloud providers are now making efforts to improve the security of their services. But you still need to be careful by verifying whether the service provider is implementing a safe identity management system‚ privacy protocols‚ and database security.
2. Password Security
The more people access a cloud account‚ the more it becomes vulnerable. If someone hacks your account or gets hold of your password‚ they can access your information. However‚ organizations can use two-factor verification and other security measures to protect their passwords. Also‚ when an employee resigns‚ the wise thing to do is to modify all passwords.
3. Cost Management
With cloud computing‚ users can quickly access apps on the internet without having to purchase‚ maintain‚ and manage any costly software or hardware. The option is cost-effective but the challenging and more costly aspect is tuning the needs of an organization on a third-party site. Also‚ moving data to a public cloud could be too expensive especially for small businesses or projects.
4. Lack of Skilled Workers
As more people move their activities to the cloud‚ the need to improve cloud tools as well as manage the entire process arises. This explains why the labor market consistently demands people who have IT skills. Some firms train their in-house staff to be able to handle this challenge.
5. Internet Connectivity
Cloud services require high internet speed‚ which may not be readily available to most small businesses. Hence‚ small businesses need to invest in good internet connections to prevent downtimes that might lead to business losses.
6. Private Cloud
Creating a private cloud has its advantages because the company's data will remain in-house. But the IT team must be able to build everything and fix all the problems that will arise. They also need to ensure the cloud functions seamlessly‚ automate all manual tasks‚ and execute those tasks correctly. Setting up an in-house cloud sounds like an elephant project‚ but that is the future of cloud computing.
What are the threats to Cloud Computing?
1. Unauthorized Access
Cloud deployments are not within the company's immediate environment and can be accessed from public internet. Although staff members and customers can easily access it‚ an attacker can gain access to it too. Issues like compromised credentials or improper security configuration enable hackers to have unauthorized access without the knowledge of an organization.
2. Account Hijacking
A lot of people have weak passwords and as they use and reuse those weak passwords on different platforms‚ it becomes easy to access their personal data because one stolen password is a gateway to accessing different accounts.
Hijacking an account is a very serious security threat as more people rely on cloud infrastructures. If a hacker has the credentials of an employee‚ they can access sensitive data. Also‚ accessing the credentials of a customer can give hackers access to a company's online account. The more troubling part is that most organizations are yet to learn how to identify threats and respond to them effectively.
3. External Data Sharing
Cloud computing makes it easy for people to share data. You can invite team members to collaborate with you on a project by sending a direct email or sharing a link. This idea facilitates remote work but it is a major threat to cloud computing.
Using a link to share data is easier than inviting individual collaborators. But anyone can get hold of the link and access your data without your knowledge. Also‚ you cannot set your link to be accessible to only one recipient. That recipient can forward your link to other people.
Cloud Management in Cloud Computing

Cloud management in cloud computing involves controlling and maintaining online resources and services whether they are hybrid‚ public‚ or private. Some aspects of cloud management include deployment‚ capacity‚ backups‚ storage‚ performance‚ and load balancing. To carry out these tasks‚ a cloud manager requires access to the functionalities in the cloud.
Nowadays‚ big organizations prefer cloud storage as their basic data store. A little error or short downtime can result in inconvenience and loss for such organizations. Therefore‚ to maintain cloud computing services‚ specific people should ensure that things work as expected.
The mandatory cloud management activities include:
Auditing Backups
Backups should be audited at intervals to ensure that files of users are randomly restored. The service provider or the organization can carry out this task.
Data Flow
Cloud managers are tasked with the duty of designing a diagram that shows how data should flow within an organization.
Lock-In Vendor
Managers are supposed to move the data of their organizations from one server to the other in case they decide to switch to another provider.
Knowledge of Security Procedures
Managers should be aware of the service provider's security plans especially encryption and employee screening policies‚ e-commerce processing‚ and multitenant use.
Monitoring the Scaling‚ Capacity‚ and Planning Abilities
Managers should know whether the service provider will meet the demand of their organizations in the near future as well as their ability to scale.
Audit Log Monitoring
Managers need to audit logs regularly to identify any errors in the system.
Testing and Validating Solutions
Testing cloud services is necessary to ensure they are functioning as planned. Also‚ verifying the results of the tests leads to the creation of error-free solutions.
How Cloud Computing Can Help Financial Institutions
1. Continuity Risk and Reduced Data
Cloud computing offers a valid alternative to outdated systems that are vulnerable to phishing. It has the potential to identify potential breaches with its embedded security that safeguards banking data. Cloud computing also provides backup for improving disaster recovery.
2. Greater Agility
Credit unions and banks that want to achieve more agility in business can utilize cloud technology to instantly respond to dynamic market conditions. They can also leverage applied analytics and real-time data to achieve the benefits of operational productivity and customer experience. From allowing technology scalability to competitive dynamics‚ there are boundless opportunities.
3. Enhanced Innovation
The development cycle of products can be shortened with cloud computing. This will allow financial institutions to test products as well as react to the responses of customers quickly.
Additionally‚ cloud computing facilitates the possibilities of open banking‚ thereby‚ expanding the set of solutions available to customers across non-traditional and traditional financial services.
4. Improved Efficiency
Most financial institutes struggle to automate‚ streamline‚ and connect their back office in order to improve customer experiences. However‚ cloud technology could help to aggregate operational systems and multiple data that impede efficiency. Therefore‚ the time spent on searching for insights can be channeled to more impactful and productive analysis as well as decision-making.
5. Increasing Customer Insights
Businesses derive insights from the data of their customers. These can only be gotten with high-level analytics‚ and the results provide a foundation for a type of proactive engagement and personalization that is not possible when using a legacy infrastructure.
With the availability of these insights in real-time‚ banks can better understand how individual customers behave‚ what triggers actions that build loyalty‚ drive conversion‚ and increase engagement.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Computing Provider for Your Business
Choosing a service provider for cloud computing might be quite difficult because of the large number of companies claiming to offer the best services. However‚ here are some tips to help you choose the right company:
1. Read the Fine Print
One thing to look out for is when a company urges you to sign a contract that you may not fully understand. That is a huge warning sign.
A good company should take time to help you understand the guidelines and what the contract covers. You should also know what the contract does not cover in case anything breaks‚ you would know who should fix it.
Additionally‚ the company won't force you to sign a contract especially when you are not sure of the details. Therefore‚ you must be careful to read through and understand a document before agreeing to do business with a company.
2. Find Out What is Guaranteed
You may enter into an agreement with a company and they won't deliver as promised. In that case‚ what can you do? That is why you need to find out what the company is guaranteeing you. You should also know whether you can back out‚ when‚ and how to terminate the contract.
3. Familiarize Yourself With Their Feedback Loop
Communication is essential in all relationships; this also applies to the relationship you have with any service provider you choose. When choosing a service provider‚ look out for how they accept feedback and if they even accept feedback from clients.
Find out whether they ask customers to complete surveys or schedule regular checks to ensure they're meeting your expectations. Whichever method they use‚ ensure they listen when customers give constructive criticisms or honest concerns.
4. Ask About Security
When it comes to the cloud‚ security is a major concern. Hence‚ you need to find out how the company protects the data of its clients. You can ask detailed questions related to your peculiar use case‚ regulatory requirement‚ and industry.
Additionally‚ you should find out the particular area that the company is responsible for‚ including your own role in providing security for your information.
Some security features are free while others aren't. So‚ the company should tell you the extra paid services they provide and where a third-party app is necessary. Google Cloud simplifies the process by listing their partner integrations‚ paid products‚ and security features on their website.
5. System Management
Before selecting a cloud service provider for your business‚ you have to consider the types of cloud platforms and what it takes to manage them. Each platform supports different tools‚ architecture‚ and integration with other services.
If there are specific services that your business cannot do without‚ you need to be sure that the provider you use can integrate them easily. Else‚ you should be ready to port to another service that supports them. You should also take time to find out how long it will take your IT team to manage different aspects of the infrastructure before arriving at a decision.
6. Costs
Of course‚ this is not the most important point to consider‚ but we know that it plays a significant role in determining the service provider to use for your business. Different companies have different pricing structures. So‚ you need to look at the associated costs alongside the sticker price.
For instance‚ AWS utilizes a pay-as-you-go method‚ Google Cloud charges per second‚ and Azure bills on-demand. Therefore‚ choose a provider according to your usage pattern.
What about cloud computing security?
Cloud computing security is the practice of protecting information‚ data‚ applications‚ and cloud computing environments. It aims at securing the cloud against unauthorized access‚ malware‚ hackers‚ and DDOS (distributed denial of service) attacks.
Although cloud security relates to security for the cloud‚ cloud-based security is a SaaS model of delivering security services. It is hosted in the cloud instead of being deployed through on-premise software or hardware.
What is the future of cloud computing?

Virtually everything today can be connected to the cloud. It opens a new world for platforms‚ services‚ applications‚ and jobs. The future of cloud computing is a combination of on-premise and cloud-based products‚ which gives rise to hybrid solutions.
This modification is flexible and scalable‚ providing control and security for the data center. Cloud has several features that make its future bright in the industry. Below are some predictions from current usage and trends.
1. Modular Software
Individual programs and their complexity are increasing regularly. As a result‚ cloud technology may soon require advance thinking. In the future‚ people may need to store data in other places apart from the cloud. Hence‚ modules would be required to store applications on the servers of different cloud services.
2. ModularIncrease in Storage Capacity
The amount of data we generate these days is overwhelming. It is even becoming more difficult to store data safely. However‚ because many companies are subscribing to cloud computing‚ it is predicted that many data centers will be created. The competition will become even tougher as these centers will offer very low prices to attract more customers.
3. Enhanced Internet Performance
IoT is helping to improve the quality of internet connectivity. When combined with cloud computing‚ data can be stored in the cloud to enhance analysis and performance. Hence‚ users should expect fast-loading applications and services. The network will be faster and data transfer will be quicker.
4. Enhanced Security
Currently‚ the data on the cloud is not completely secure because the companies providing the services may not offer proper security. Hence‚ in the future‚ we should expect better security.
Conclusion
Despite the benefits and drawbacks of cloud computing‚ it remains the fastest-growing aspect of network-based computing. It offers a lot of benefits to small and large businesses‚ simple users‚ and programmers.
Traditional computing is already obsolete because‚ with cloud computing‚ you can access new applications quickly and enjoy frequent updates without buying and installing any software. Cloud computing has a promising future‚ and it has come to stay.












